 Craig Adams / 15min read
Craig Adams / 15min read
SEO is Dead!
If I had a penny for every article, blog, research piece that has proclaimed that ‘SEO is dead’ to the masses, I certainly would not be writing this article.
Alas, despite the nay sayers, SEO is far from dead. To echo SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) expert and self-professed “father of SEO” Bruce Clay,
“SEO is dead when Google stops changing things and all of your competition dies”
Until such time as the Google’s Algorithms become static and your competition passes on (may they rest in peace), we have compiled this self-help SEO guide for retail eCommerce business. In the next 12 minutes, you will learn the basics of eCommerce website SEO, from keyword research and strategy development to category & content optimisation.
In this piece, we focus on category optimisation for eCommerce websites. Why you might ask? When optimised, category pages are powerful customer acquisition pages for ecommerce websites.
They acquire individuals who have yet to decide on what product best meets their needs. Product pages on the other hand, capture a much more refined audience when customers have a very clear picture of the product they require.
Product page SEO is important but there are potentially better returns on investment from category based SEO. For 90% of retail companies their first foray into Search Engine Optimisation should begin with category optimisation.
![]()
Who should read it?
Business Owners, Digital Marketers, Traditional Marketers. Quite literally anyone with a vested interest in Selling Online.
Focus/Primary Keywords – A word or phrase that best describe the content of a webpage or category. In essence this is the terms that you want your webpage to show for when it is used by a person in a search engine.
Meta Title –The title of the web page in question and an incredibly important piece of information for search engines, when choosing whether or not to show your page in its search results. Meta title’s show in search results pages as the main link to a web page.
Meta Keywords – These help search engines like Google understand the topic of webpage. Users typically don’t see meta keywords when searching.
Meta Description – A meta description, is typically a short, concise description of website content that help search engines understand a page content. They also appear in search results pages under the page title.
SEO – Search Engine Optimisation or the actions an individual takes to help a website be found in search engine results pages.
Image Alt Text – Alternative text that is displayed in place of an image should there be an issue loading the image.
Keyword Planner – A free tool from Google that showcases the amount of times a particular keyword is searched for every month.
Moz – Search Engine Optimisation software that mimics the actions of Google and can help improve website efficiency.
Short Tail - A search term or keyword that contains less than 3 words
Long Tail – A search term or keyword that contains more than 3 words.
Heading’s (H1) – Headings help search engines and users to read the content of a page.
URL – The address of a webpage.
SERP –Search Engines Results Page
CTR – Click Through Rate
Hyperlinks – A link to another website or web page from your website.
The first challenge for any eCommerce business is to research the keywords their customers are using and begin to develop their websites keyword strategy. There are a number of free & paid tools which we will now examine.
A free tool from Google Keyword Planner through Google AdWords can prove an invaluable resource for keyword research. Accessed through your AdWords account, the Keyword Planner Tool offers two options when it comes to keyword research: Find new Keywords by exploring themes and topics relating to your website or Examine Search Volumes for a chosen set of keywords. The second option is “Get Search Volume & Forecasts”tool which will show you projections and costs from a pay per click perspective, with little or no value from a search engine optimisation perspective.
From the off, we recommend utilising the Find New Keywordsoption to explore the patterns of search chosen by potential customers. Doing so can help you compile a bank of keywords relating to the product/service in question which can be subsequently broken out into themes based on your website categories to help develop the overall strategy.
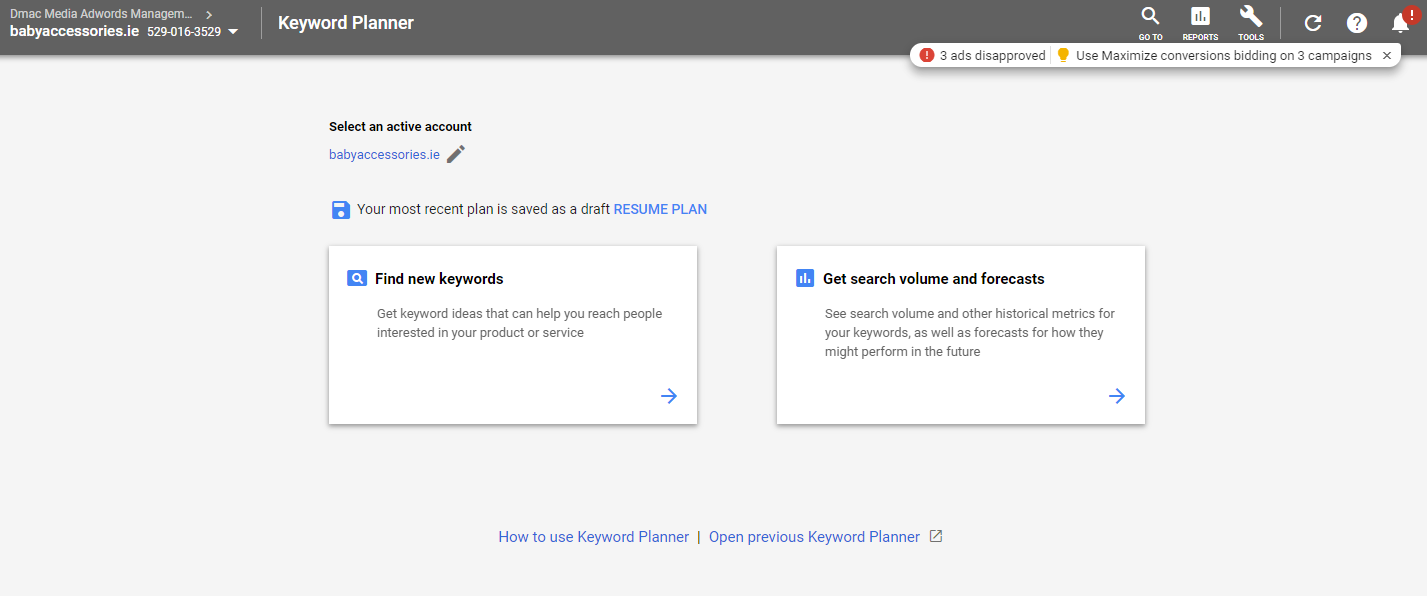
Fig 1.1 – Keyword Planner offerstwo optionsfor Keyword Research
Accessing the keyword planner can be done by logging into the AdWords account, and selecting keyword planner under the Tools > Planning sections in top menu on the interface.
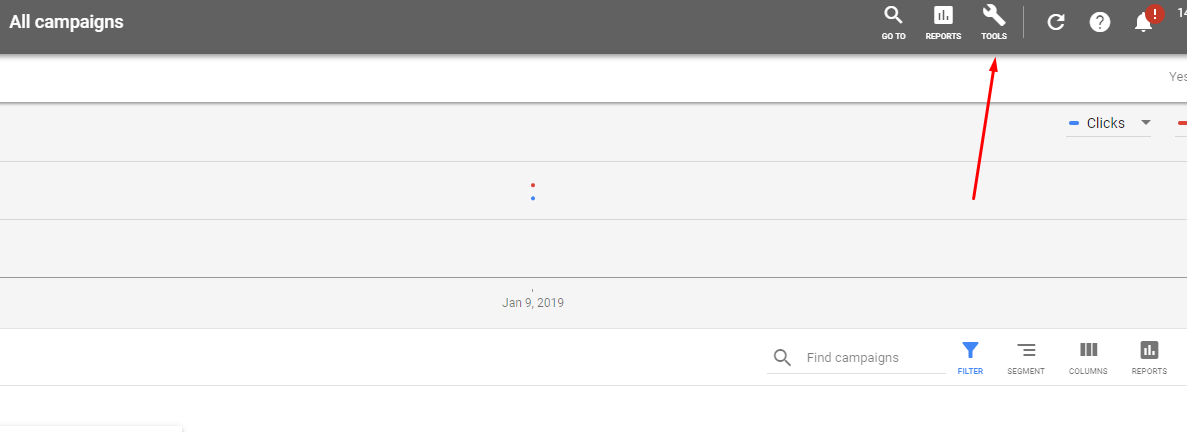
Fig. 1.2 – Accessing Keyword Planner is done through the Tools Option on the interface
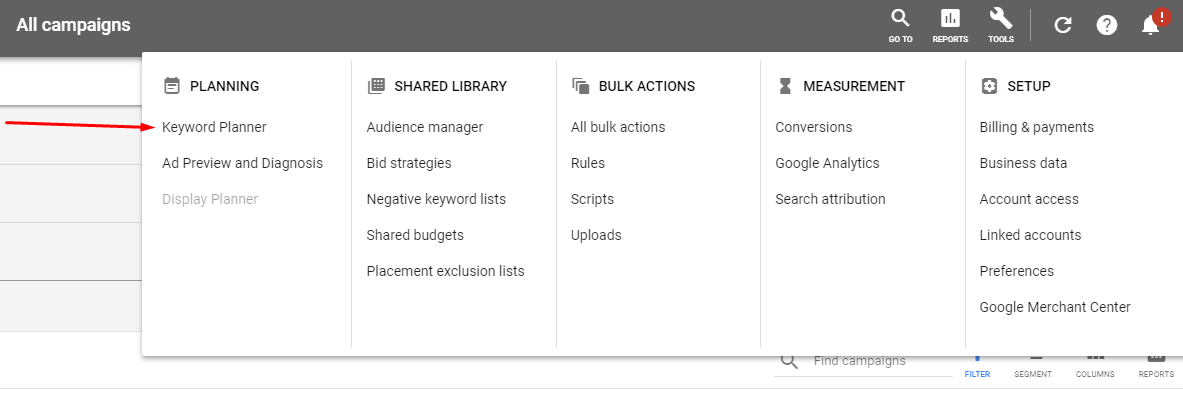
Fig 1.3 – Keyword Planner is located under the Planning Section in the Tools Drop Down Menu.
A valuable resource when planning online sales events, keyword optimisation & sales promotion. Google Trends showcases the relative search volume forup to 5 keywords or topics over a chosen duration. Look back over the last five years or so to develop consumer insightand buying behaviour using Google Trends, and strategise for sales promotion & optimisation for the year ahead. Another Free Tool from Google, Trends should be the second port of call before developing a keyword strategy for the website and will help determine the areas to focus on.
Fig. 1. 4 – Google Trends Offers Valuable Consumer Insight
Ideally, category optimisation should be carried out when products relating to that category is out of season, as gaining rank for keywords can take considerable time. Doing so, lessens the negative impact of potential changes on both traffic and revenue.
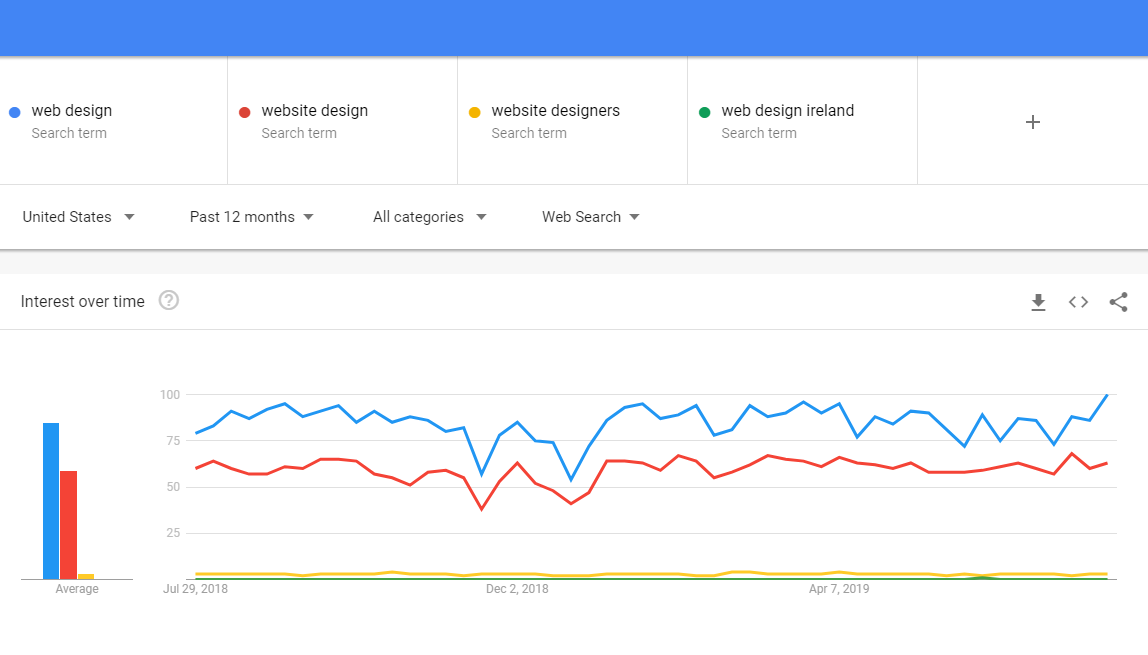
Fig. 1.5 – Compare Search Interest for up to 5 Keywords or Topics using Google Trends.
 Learning Point
Learning Point
It is important to understand the difference between Topic & Search Term targeting when it comes to Google Trends. Choosing a Topic will return information about searches relating to the particular topic. Choosing London, for instance, will include data from searches such as “Capital of the UK.” Choosing Search Term targeting on the other hand will showcase information about searches containing that search term. For instance, in the example above, the search term car seat returns highest volumes because it collates information about any search containing the words “Car Seat.”
Moz offer both paid and free versions of their Keyword Explorer tool. The Free Version allows the users to research up to 10 keywords per month and offers invaluable information when compiling a primary keyword list. Users can avail of metrics such as Average Monthly Search Volume, Perceived Difficulty of Ranking on the First Page & the Expected Click Through Rate should you be able to rank on the first page.
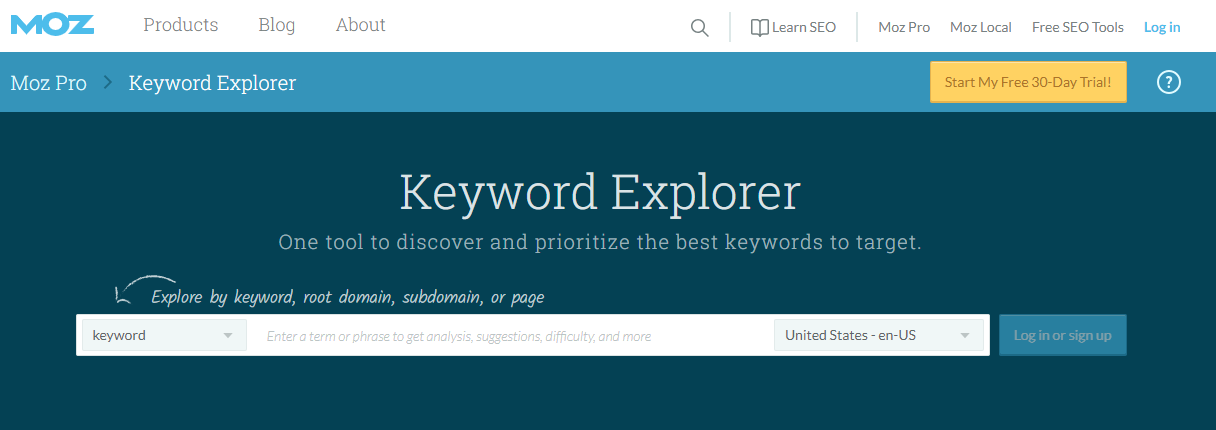
Fig. 1.6 – Moz’s Keyword Explorer Tool offers a 30-day free trial.
Ideally, when utilising Keyword Explorer you should aim for a High Volume, Low Difficulty, and High Exp. Click through Rate keywords wherever possible.
 Learning Point -
Learning Point -
As with all keywords, choosing long tail (more than 3 words) will result in lower search volumes but should also be easier to gain first page position. Long tail keywords are also likely to have a higher percentage click through rate over short tail keywords.
Having carried out research and created a database of potential keywords, it is now time to develop and create your category & sitewide keyword strategy. Keyword Strategies are designed to help ensure that each individual category of the website is assigned a relevant set of keywords that accurately describe the pages content.
 Learning Point -
Learning Point -
To develop this strategy, we recommendcollating category keywords by theme initially. For instance, under a category entitled “What We Do”, Dmac collate a wide variety of keywords (both long and short tail) relating to the theme of Web Design. (Web Design, eCommerce Web Design, Website Design Company Ireland etc.)
The chart below demonstrates the best approach todeveloping a keyword strategy for a multi-tier eCommerce Website.
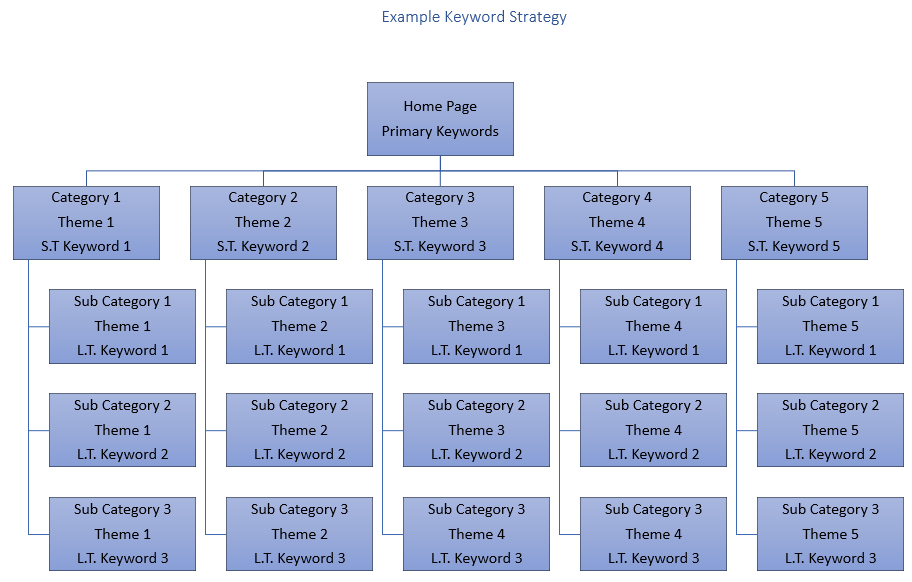 Example Keyword Strategy
Example Keyword Strategy
Once a sitewide keyword strategy has been created for categories, it is now time to begin optimising each category for each of the chosen keywords to give it the best chance to rank organically in search engines. In order to optimise a category page for a chosen keyword, there are a number of elements we must concern ourselves with, each having their own unique set of characteristics and best practices. These include, Page Titles, Meta Keywords, Meta Descriptions, Heading or H1’s, On Page Content, Links, URL’s & Images.
The page title is among one of the first indicators for search engines when evaluating the web page content.
 Learning Point -
Learning Point -
For the most part, page titles are not seen by users once on the website, however they are imperative in getting a user to the website. Page titles for categories are showcased in the search engine and appear as the blue text on Google.
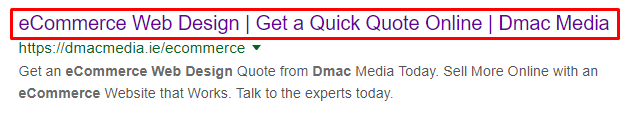
Fig. 1.7 – Page Titles can determine whether or not a user clicks on a link in SERP’s.
Updating your Category Page title can be done in the admin section of your website and selecting the Category SEO Option with your chosen page/category. Doing so will bring up the pop as per the figure below and editing the content in the field next to Title, will update the page titles associated with this category.
Disclaimer–We are going to assume you are using the Dmac Media CMS. If not, you should really be asking yourself why.
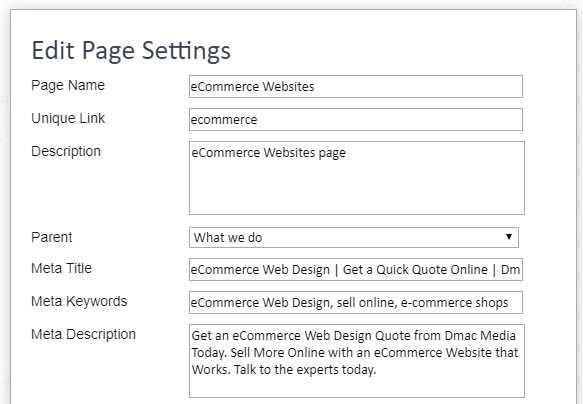
Fig. 1.8 – Editing the content in title will update the category page title.
While there is no Category Title character limit, Google only displays the first 60 characters of a title tag. Ensuring your title tag is under 60 characters ensures users will see all the information you include.
 Learning Point -
Learning Point -
The rule of SEO is to include the focus or primary keyword early in your meta title.
. Research carried out by Moz SEO Software found that keywords closer to the beginning of your title may have more impact on search rankings. So, if you really want your category to rank for a particular keyword include it early in the title.
Title tags should not only accurately describe what the user can expect on the page in question but should also appeal to them wherever possible. Including keywords that appeal the potential consumer as a secondary element can help improve click through ratesfrom organic searches as keywords included in the users search will appear as bold in the results page.
Including your brand name as the final or tertiary element of the title tag can helpimprove brand recognition and awareness of who you are in the SERP’s. Be mindful however of how your categories are appearing in results, as Google may append your brand name to the end of search results automatically, if it results in a Higher CTR.
A now defunct meta tag for Google, Meta Keywords may still have a very small impact on organic ranking. Feel free to leave these out if time doesn’t allow when optimising the categories. If time is on your side, simply add three keywords that reflect the variations you would have included in the page title and bobs your uncle.
Similar to Page Titles, Meta Descriptions appear on search engine results pages below the blue text. These too can be edited through the category SEO settings in the Dmac Admin section, in the same fashion as page titles & meta keywords.
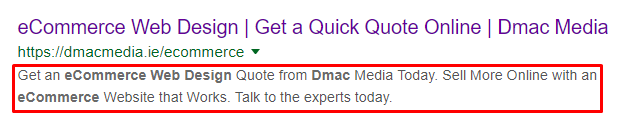
Fig. 1.9 – Meta Descriptions are showcased in the Search Engine Results Page.
 Learning Point -Meta descriptions should be a string of sentences that describe what the user can expect by clicking on the link. Include the primary or focus keyword in your meta description where possible as these will appear in bold when triggered by a keyword and improve overall relevancy for the user. Where possible, also include a call to action or elevator pitch in relation to your business.
Learning Point -Meta descriptions should be a string of sentences that describe what the user can expect by clicking on the link. Include the primary or focus keyword in your meta description where possible as these will appear in bold when triggered by a keyword and improve overall relevancy for the user. Where possible, also include a call to action or elevator pitch in relation to your business.
Google can only showcase the first 160 characters of a Meta Description, so ensuring you can communicate your message within these constraints is key.
Headings give web page content structure and are aesthetically pleasing when it comes to user experience. Correct use of headings on web pages also pleases search engines and can reinforce keywords of choice, thus improving ranking. Headings are numbered 1 – 6 with each varying slightly in appearance.
 Learning Point - Heading 1’s are without doubt the most important, while the subsequent headings can be used to effectively break up written contenton web pages. For an eCommerce website effective use of heading 1’s on category pages is essential. Keep heading 1’s (or H1’s) interesting and appealing to the user. They should also immediately reinforce the keywords that prompted the user to click in the first place subsequently minimising bounce rate.
Learning Point - Heading 1’s are without doubt the most important, while the subsequent headings can be used to effectively break up written contenton web pages. For an eCommerce website effective use of heading 1’s on category pages is essential. Keep heading 1’s (or H1’s) interesting and appealing to the user. They should also immediately reinforce the keywords that prompted the user to click in the first place subsequently minimising bounce rate.
Unlike Page Titles & Meta descriptions there is no desired length for H1’s however, clear concise messaging tends to work best.
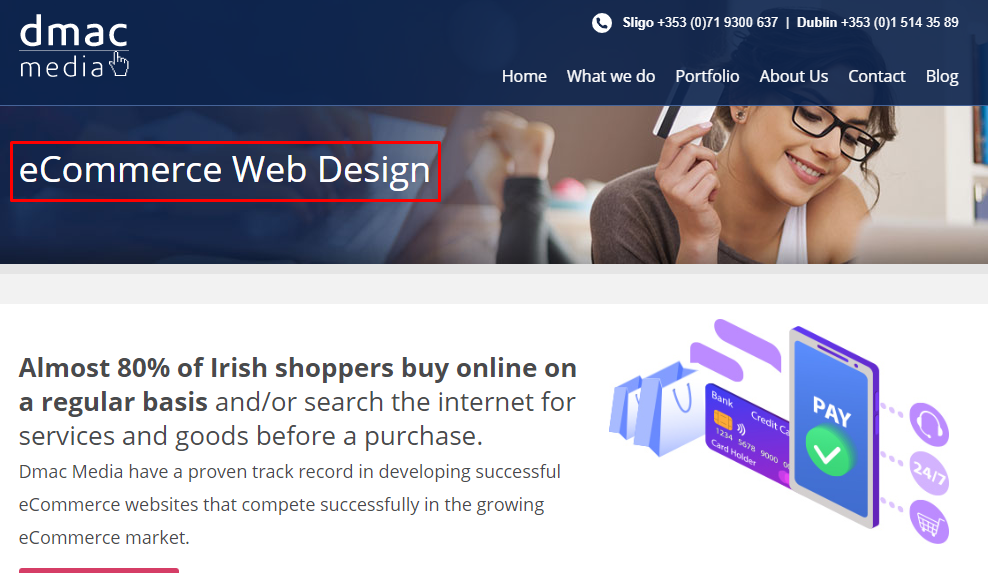
Fig. 1.9 – Heading 1’s can give website categories structure and improve bounce rate.
On page content can prove an invaluable resource when it comes to organic ranking. Adding between 200 & 300 words of content to each category page improves overall organic ranking and adds opportunities to include a range of additional and supplementary keywords.
 Learning Point -Unique useful content is key to creating good on-page category content. Including supplementary phrases or keywordsthat are of interest to the customer such as brand names are also a key consideration. Feel free to add some sales elevators also, to help your visitor become your customer.
Learning Point -Unique useful content is key to creating good on-page category content. Including supplementary phrases or keywordsthat are of interest to the customer such as brand names are also a key consideration. Feel free to add some sales elevators also, to help your visitor become your customer.
Ideally, extensive written content should not appear above products where possible. Category headers can include a Heading 1 and an image but should not detract from products. Category content should appear below products on a product category wherever possible.
When including keyword in on page content, care should be taken not to fall victim to keyword stuffing. Try to include atarget keywordor variation 3 to 4 times only.
Linking content internally can have a positive effect on overall SEO. Internally linking content contributes toeasieruser flow and leveraging strategic anchor text. (i.e. the text that links to the page) can improve overall SEO. Aim to include 2 – 3 internal links to relevant categories, that may help the end user.
URL’s should, where possible, include the category focus keyword. Having a clear, concise URL structure is integral to improving organic ranking. Not only should URL’s be relevant to search engines, they can also communicate key information to the end user. Your Dmac Media CMS creates these clear andconcise URL’s using your category name by default. Should you wish to change the category URL to include a more relevant keyword, remember to use a 301 redirect from the old link to the new link.
Doing so, negates the impact of the change and passes link juice from the old URL to the new URL, meaning the change should have little impact on the overall performance of the category.
Category images aid overall user experience and candecrease bounce rate. Having an aesthetically pleasing category image, reinforces the category content, meaning users aremore likely to consider the products on site.
Ensure category images are size optimised when created by using tinyjpg.com. Once uploaded, remember to add alt-text to the image. Alt Text displays should image fail to load or if the users are using a screen reader or browser that blocks the image.
 Learning Point -Despite the many advances in Search Engine Technology in recent years, Search Engines cannot “see” an image. Alt Text helps search engines understand the nature of the image.
Learning Point -Despite the many advances in Search Engine Technology in recent years, Search Engines cannot “see” an image. Alt Text helps search engines understand the nature of the image.
Best practice for image alt text is to accurately describe the contents of the image, in a short concise fashion and where possible, include keywords.